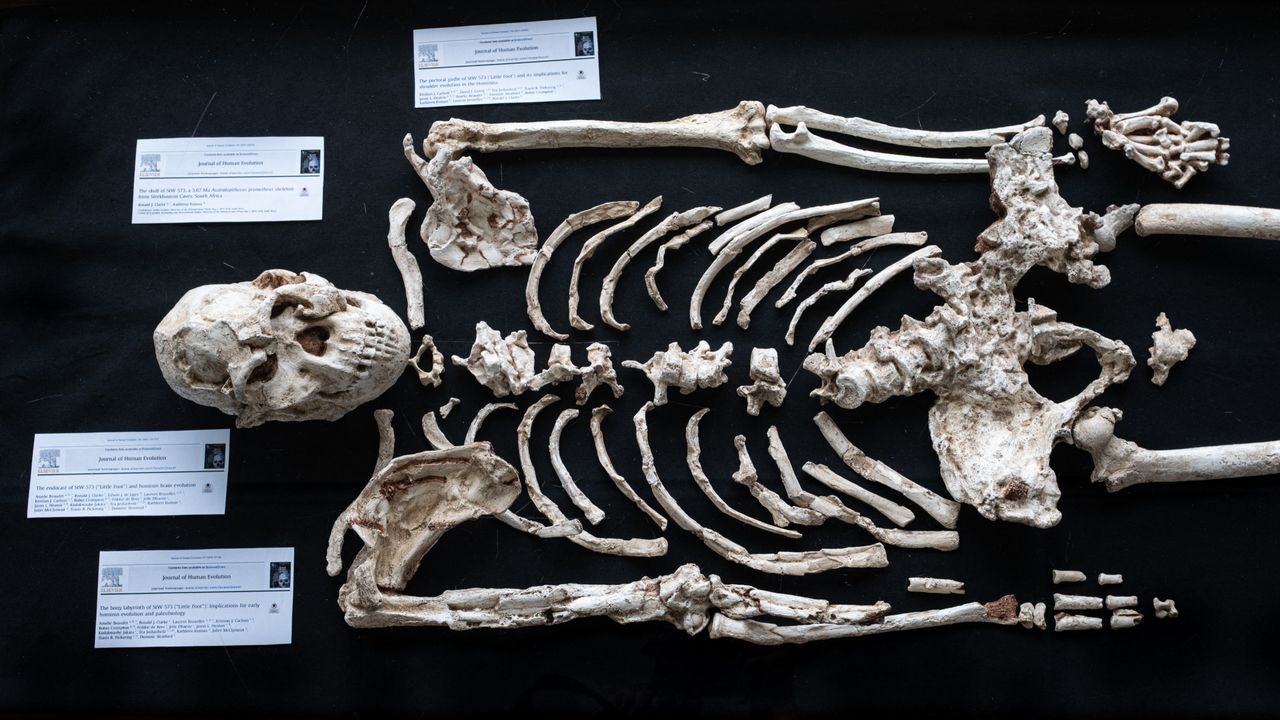
New research suggests that the well-known hominin fossil, known as Little Foot, may represent an unknown human ancestor. This finding could reshape our understanding of human evolution. The study, published in the American Journal of Biological Anthropology, challenges previous classifications of the fossil, which is considered one of the most complete Australopithecus skeletons ever discovered.
Unveiling Little Foot’s Ancestry
Little Foot, a nearly complete skeleton unearthed in South Africa, has intrigued scientists since its initial reveal in 2017. The fossil was found in the Sterkfontein Caves, located within the UNESCO World Heritage Site known as the Cradle of Humankind. While researchers have debated its exact place in the human lineage, recent analysis points to the possibility that it could belong to a previously unidentified species.
Some researchers have suggested that Little Foot should be classified as Australopithecus prometheus, a name previously used for another fossil discovered in 1948 but later deemed unsuitable. Others have proposed that it might be part of the known species Australopithecus africanus. The new classification claims, however, assert that neither of these categories accurately describes Little Foot.
The implications of this research extend beyond academic interest; they may influence how we view the evolution of early humans. The debate among anthropologists over the classification of human fossils often leads to intense discussions, and this study is likely to provoke significant reactions from the scientific community.
Recent Highlights in Scientific Discoveries
In addition to the intriguing findings regarding Little Foot, the weekend brought a peak in the Geminid meteor shower, which dazzled skywatchers around the globe. This annual event is known for its bright meteors and is considered one of the best meteor showers to observe. For many, it provides a unique opportunity to engage with the wonders of the universe.
Moreover, the interstellar comet 3I/ATLAS is making its closest approach to Earth this week, further captivating both amateur and professional astronomers. As these celestial events unfold, they remind us of the dynamic nature of our universe and the ongoing importance of scientific inquiry.
For those interested in more scientific developments, recent stories have highlighted the sequencing of the vampire squid’s genome, shedding light on this ancient creature’s biology. Additionally, the discovery of a 2,000-year-old shipwreck in the Mediterranean may reveal insights into the maritime history of ancient Egypt.
As these stories develop, the scientific community continues to explore the mysteries of our past and the cosmos, contributing to a deeper understanding of both human evolution and the universe we inhabit.