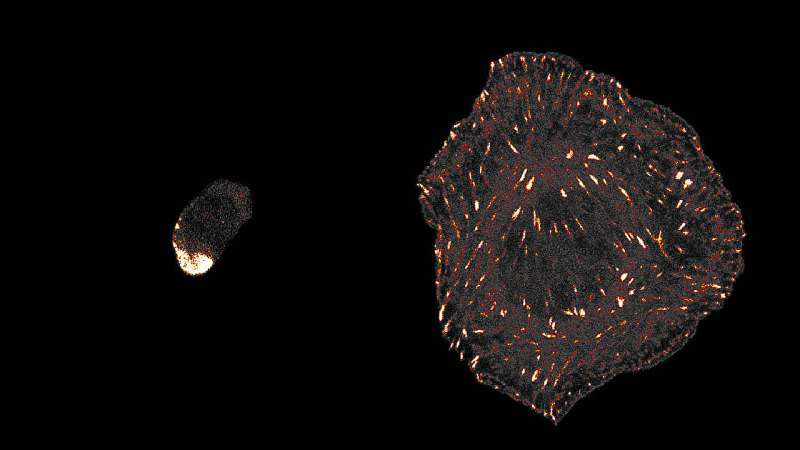
Researchers from Singapore, France, and the United States have made a significant advancement in wireless technology by developing a compact antenna designed to handle information-rich terahertz (THz) signals. This innovative design, reported in the journal Nature Photonics, could play a crucial role in the evolution of sixth-generation (6G) wireless networks, enabling data transmission at unprecedented speeds.
The research team, led by Ranjan Singh from the University of Notre Dame, leveraged concepts from topological photonics to create an antenna that is both efficient and compact. Traditional antennas often struggle with high-frequency signals, particularly in the terahertz range, which is essential for the high data rates expected from future networks. The new design addresses these challenges, potentially paving the way for faster and more reliable communication technologies.
Potential Impacts of the Antenna Design
As the demand for faster wireless communication continues to grow, the development of this antenna could be a game-changer for various industries. The capacity to manage THz signals efficiently may facilitate advancements in applications ranging from enhanced mobile broadband to the Internet of Things (IoT). The research highlights the importance of integrating topological concepts in engineering to improve signal processing capabilities.
In their findings, the team notes that while the current design is promising, further refinements are necessary before it can be deployed in real-world applications. Continuous research and development will be essential to overcome existing technological barriers and ensure compatibility with emerging standards for 6G networks.
Future Directions for Wireless Technology
The move towards 6G is already underway, with major telecommunications companies investing heavily in research and infrastructure. The ability to transmit data at extremely high speeds will not only enhance user experiences but may also support new technologies that require robust communication networks. As the global landscape shifts towards more interconnected devices, the implications of this research extend beyond just telecommunications, influencing various sectors including healthcare, transportation, and smart cities.
The collaborative effort across countries underscores the importance of international cooperation in addressing technological challenges. By harnessing the principles of topological photonics, researchers aim to unlock new possibilities for wireless communication that could redefine how we connect and share information in the future.
As this research progresses, the potential for real-world application grows, promising a future where connectivity is faster, more reliable, and more efficient than ever before.