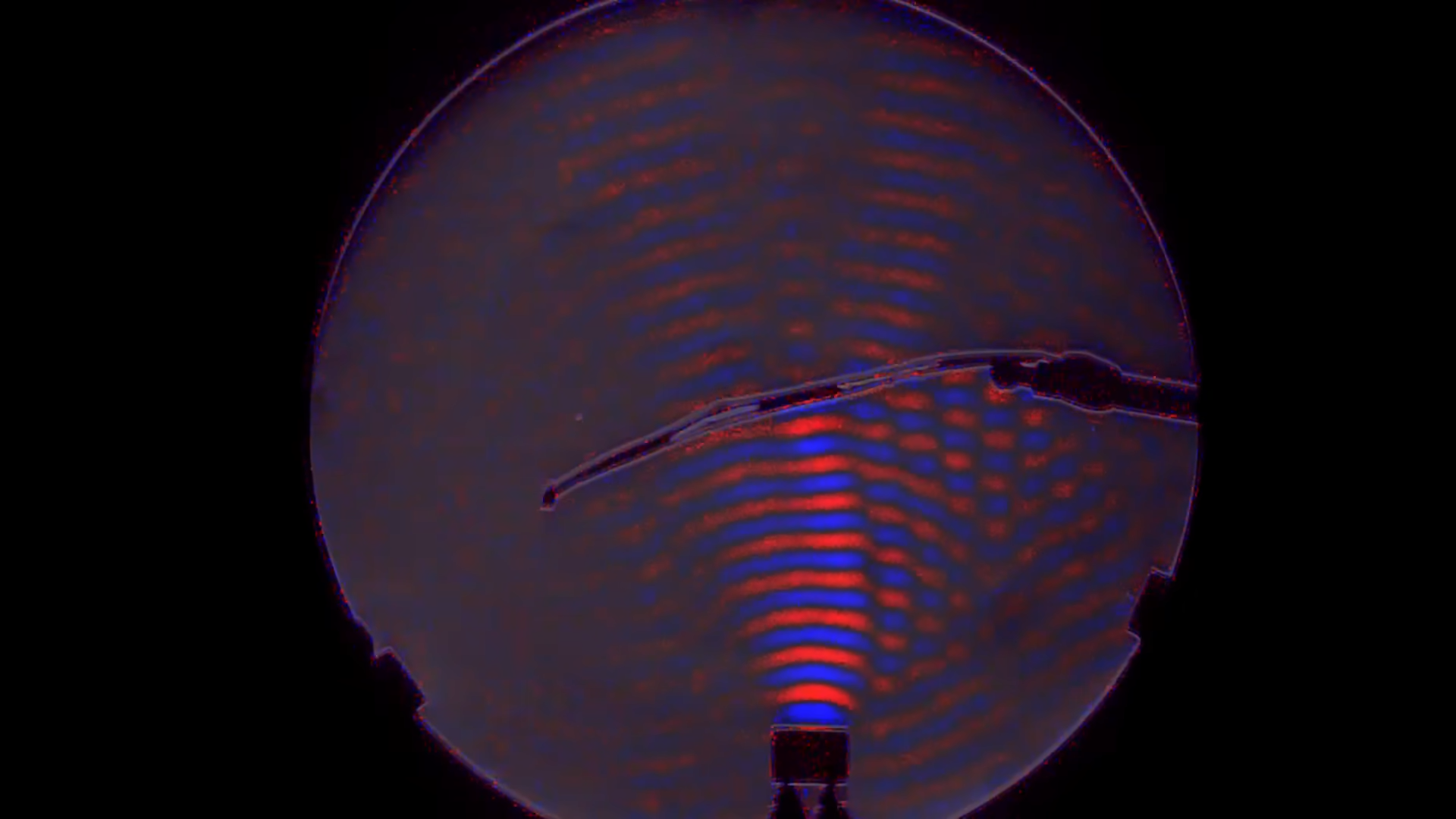
Researchers at Rice University have unveiled a groundbreaking achievement in the study of Alzheimer’s disease by creating the first complete, label-free molecular atlas of the brain affected by the condition in an animal model. This innovative atlas provides critical insights into the mechanisms underlying the onset and progression of a disease that claims more lives than both breast cancer and prostate cancer combined.
The molecular map represents a significant advancement in understanding how Alzheimer’s disease develops over time. By employing label-free imaging techniques, the research team was able to analyze the brain’s complex biochemical landscape without the interference of traditional labeling methods. This approach allows for a clearer view of molecular interactions and changes that occur in the brain as Alzheimer’s progresses.
Understanding Alzheimer’s Through Molecular Mapping
The research team utilized advanced imaging technologies to identify various metabolic signatures associated with Alzheimer’s. These signatures could provide valuable clues regarding the disease’s early stages, potentially leading to new therapeutic strategies. According to the research, understanding these metabolic alterations is essential for developing interventions that could slow the disease’s progression or prevent its onset altogether.
The implications of this research extend beyond academic interest. With an increasing global burden of Alzheimer’s—currently affecting over 55 million people worldwide—the need for effective treatments is urgent. The disease’s impact is profound, causing not only cognitive decline but also significant emotional and financial strain on families and caregivers.
Moreover, the findings from this study could pave the way for further research into other neurodegenerative diseases. By establishing a detailed molecular framework, scientists can compare Alzheimer’s with conditions such as Parkinson’s disease and Huntington’s disease, potentially unlocking new pathways for treatment.
Looking Ahead: Future Directions in Alzheimer’s Research
The research conducted at Rice University marks a pivotal moment in the quest to combat Alzheimer’s disease. The team plans to collaborate with other institutions to validate their findings and explore how these molecular maps can be translated into clinical applications. This may include the development of diagnostic tools that utilize the identified metabolic signatures to detect Alzheimer’s earlier and more accurately.
In addition, understanding the metabolic changes associated with Alzheimer’s could lead to targeted nutritional and lifestyle interventions, which are increasingly recognized as important factors in brain health. As more research unfolds, there is hope that these insights will contribute to a comprehensive strategy in addressing Alzheimer’s disease, ultimately improving the quality of life for millions of individuals and their families.
As the global health community continues to grapple with the challenges posed by neurodegenerative diseases, innovations like this molecular atlas from Rice University represent a beacon of hope. The ongoing commitment to research in this field may lead to breakthroughs that change the narrative around Alzheimer’s, providing not just answers, but solutions that could transform the lives of those affected.