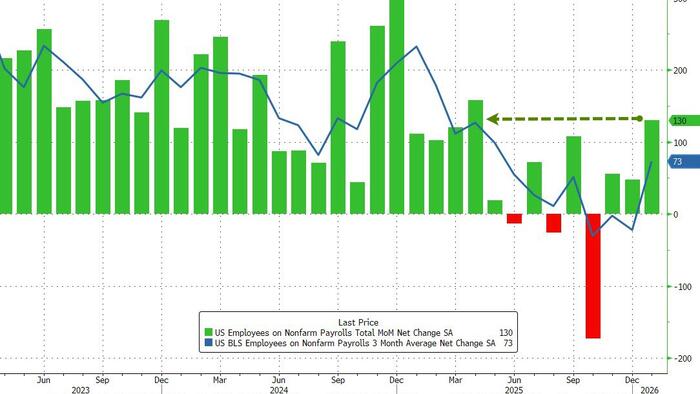
A recent study reveals that social media posts discussing unemployment can effectively predict official jobless claims up to two weeks before government data is published. This innovative analysis, conducted by researchers at the University of Southern California, highlights how online conversations about employment issues can serve as an early indicator of economic trends.
The researchers focused on posts from various social media platforms, examining how frequently users discussed unemployment and job searches. They found a significant correlation between the volume of these posts and the official unemployment figures released by government agencies. This correlation can provide valuable insights for economists and policymakers, allowing them to gauge the labor market’s health before official reports are available.
Methodology and Findings
The study utilized machine learning algorithms to analyze millions of social media posts over a specified period. By identifying keywords related to unemployment, the researchers could assess public sentiment and the likelihood of jobless claims. The results indicated that spikes in online discussions about job loss and employment challenges often preceded increases in the official unemployment rate.
Specifically, the model was able to predict changes in jobless claims with a high degree of accuracy. For example, in instances where the volume of unemployment-related posts rose sharply, actual government reports revealed corresponding increases in jobless claims. This trend was observed consistently, suggesting that social media can act as an early warning system for labor market shifts.
The implications of this research are significant. As social media continues to play a crucial role in the way people communicate, understanding its impact on economic indicators could enhance forecasting methods. Policymakers may find value in monitoring social media trends to better inform their decisions regarding unemployment benefits and economic support measures.
Broader Economic Impact
The ability to predict unemployment trends through social media analysis could reshape how governments respond to economic challenges. Traditional methods of collecting data, which often rely on surveys and official reporting, may not capture real-time fluctuations in public sentiment. By integrating social media analytics into their strategies, authorities could potentially react more swiftly to changing labor market conditions.
Moreover, this approach could empower individuals and organizations to make informed decisions regarding hiring and investment. Businesses, for instance, could adjust their strategies based on anticipated shifts in the job market, leading to proactive rather than reactive measures.
As the study highlights the potential of social media in economic forecasting, it raises questions about the reliability of traditional economic indicators. The reliance on digital platforms for insights into unemployment trends may signify a shift in how we understand and interpret economic data in the future.
In conclusion, the findings from the University of Southern California study underscore the evolving landscape of economic analysis. By leveraging social media as a predictive tool, stakeholders can gain a more nuanced understanding of the job market, ultimately benefiting the broader economy.