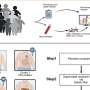
Researchers from the German Center for Diabetes Research (DZD) have successfully employed artificial intelligence (AI) to uncover blood-based epigenetic markers that signify an increased risk of complications associated with prediabetes. This breakthrough could lead to a simple blood test capable of identifying individuals at high risk of developing type 2 diabetes and its related complications much earlier than current methods allow.
Understanding Prediabetes and Its Risks
Prediabetes is characterized by elevated blood sugar levels that do not yet meet the criteria for diabetes. It is a complex and diverse metabolic disorder, making its early detection crucial. The findings from this study highlight the importance of early intervention, as individuals with prediabetes are at a significantly higher risk of progressing to type 2 diabetes, which can lead to severe health complications, including cardiovascular diseases and kidney failure.
The research team utilized advanced AI algorithms to analyze vast datasets from individuals with varying backgrounds. By examining the epigenetic modifications in their blood samples, the scientists identified specific markers that correlate with the likelihood of developing complications. This innovative approach showcases how data-driven methodologies can enhance the effectiveness of molecular medicine in diagnostics.
Implications for Future Screening and Treatment
With the ability to pinpoint those at risk through a straightforward blood test, healthcare providers could potentially implement preventive measures earlier. Such measures may include lifestyle changes, dietary adjustments, and regular monitoring, which could significantly mitigate the risk of developing full-blown type 2 diabetes.
According to the DZD, the integration of AI into the diagnostic process represents a significant advancement in personalized medicine. The study emphasizes that early detection through epigenetic markers not only improves patient outcomes but also reduces the overall burden on healthcare systems by preventing the progression of diabetes-related complications.
This research underscores the potential for combining technology and science to revolutionize healthcare practices. As the understanding of prediabetes deepens, further studies will be essential to validate these findings and assess their applicability in diverse populations globally.
The findings were published in a reputable scientific journal, marking a significant step forward in diabetes research. This work not only highlights the capabilities of AI in medical diagnostics but also paves the way for a more proactive approach to managing metabolic disorders.