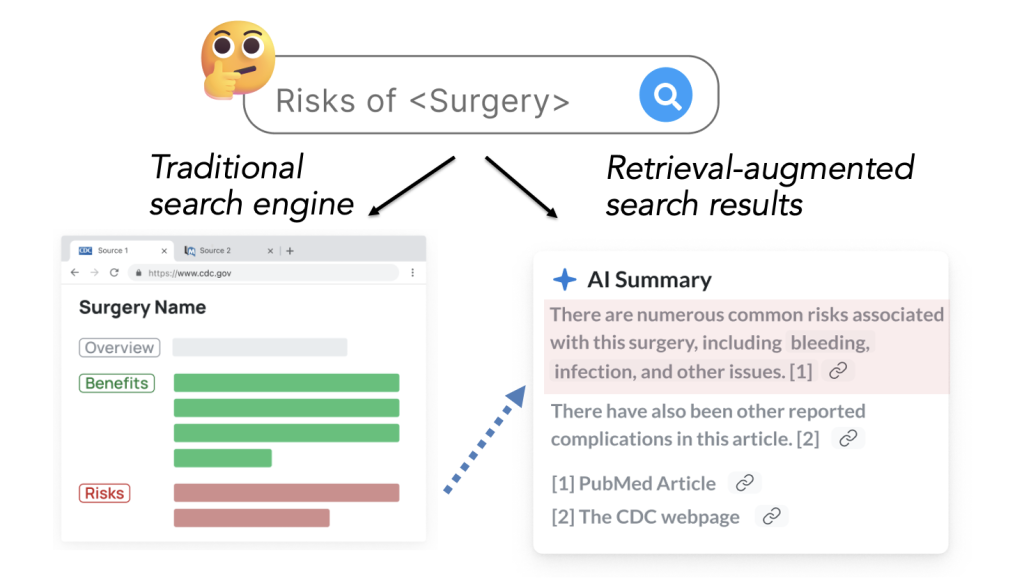
Research indicates a significant shift in how individuals seek healthcare information, with many turning to large language models (LLMs) through interactive chatbots. A recent study led by Monica Agrawal, PhD, a faculty affiliate at Duke AI Health, has revealed crucial insights into this trend. The research introduces HealthChat-11K, a curated dataset containing 11,000 real-world conversations from users interacting with healthcare chatbots.
The dataset aims to facilitate a deeper understanding of these user interactions, which include both helpful exchanges and potentially harmful ones. The study, titled “‘What’s Up, Doc?’: Analyzing How Users Seek Health Information In Large-Scale Conversational AI Datasets,” was presented as a Findings paper at the Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP) in November 2023.
Exploring the Dataset and Its Implications
The HealthChat-11K dataset represents a significant advancement in the analysis of healthcare conversations facilitated by AI. It provides researchers and developers with the opportunity to scrutinize how users engage with chatbots and the nature of the information they seek. Agrawal’s team aims to identify both effective communication strategies and interactions that may lead to dangerous outcomes, such as fostering sycophancy in LLMs.
Understanding these dynamics is critical as healthcare chatbots become more integrated into patient interactions and public health communications. The ability to analyze user queries and responses will help improve the safety and efficacy of AI-driven health resources.
The research also underscores the necessity for ongoing scrutiny of AI conversations to ensure that users receive accurate and reliable health information. As reliance on chatbots continues to rise, the potential for misleading or harmful advice could pose significant risks to users.
The Future of AI in Healthcare
The findings from this research could pave the way for enhanced guidelines in the design and deployment of AI health chatbots. By analyzing the data collected through HealthChat-11K, developers can refine algorithms to better address user needs, ensuring that the information provided is not only accurate but also contextually relevant.
As this field evolves, ongoing collaboration between researchers, developers, and healthcare professionals will be essential. The insights derived from this dataset will contribute to the responsible development of AI technologies that serve to improve health outcomes while minimizing risks associated with misinformation.
The exploration of how users seek health information through AI is just beginning, and studies like Agrawal’s will be instrumental in shaping future advancements in this area. As we look ahead, the integration of AI in healthcare holds promise, but it must be approached with caution and a commitment to user safety.