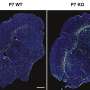
A recent study has identified a promising new treatment pathway for individuals with Shank3-related autism. Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a complex neurodevelopmental condition that affects communication, behavior, and sensory processing. The findings, published in March 2024, highlight genetic factors that may play a significant role in developing targeted therapies.
Research from the National Institute of Mental Health and the University of California, Los Angeles has shown that specific genetic variants associated with ASD can influence treatment responses. The focus on the Shank3 gene, which is implicated in synaptic function, opens new avenues for understanding and potentially treating this disorder.
Advancements in genetic research have uncovered that individuals with ASD may exhibit unique variations in the regulation of genes. This discovery is vital as it provides insight into the biological underpinnings of autism, allowing researchers to pinpoint more effective treatment strategies. The emphasis on Shank3 highlights the need for precision medicine that considers individual genetic profiles.
Genetic Variants and Their Implications
The study indicates that individuals with mutations in the Shank3 gene can display distinct behavioral traits associated with ASD. By targeting these specific genetic variations, researchers hope to develop therapies that not only address symptoms but also tackle the root causes of the disorder.
According to research published in the journal *Nature Neuroscience*, the findings could pave the way for clinical trials focused on gene editing and other advanced therapeutics. This innovative approach may lead to treatments that could enhance the quality of life for individuals diagnosed with ASD.
The implications of these findings extend beyond the laboratory. Families affected by autism are increasingly seeking personalized treatment options. As understanding of the genetic basis of ASD evolves, so too does the potential for interventions that are more tailored to individual needs.
Future Directions and Clinical Applications
Looking ahead, researchers are optimistic about the potential of developing new pharmacological agents that target the Shank3 pathway. The next steps will involve rigorous testing to ensure safety and efficacy before any new therapies can reach the market.
The collaboration between institutions highlights the importance of multidisciplinary approaches in tackling complex health conditions. By pooling resources and expertise, researchers aim to expedite the translation of laboratory discoveries into clinical practice.
In conclusion, the identification of a new treatment pathway for Shank3-related autism marks a significant step forward in autism research. As studies continue to unfold, there is hope that innovative therapies will emerge, offering new possibilities for individuals living with ASD and their families.