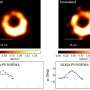
Astronomers are delving into the mysteries surrounding the powerful jets emanating from the supermassive black hole at the center of the galaxy Messier 87 (M87). This galaxy, located in the constellation Virgo, is renowned for its prominent jet, which stretches an impressive distance of approximately 3,000 light-years and can be observed across the entire electromagnetic spectrum.
These jets are composed of charged particles that are expelled from the galaxy’s core, driven by the immense gravitational forces of the black hole, which has a mass estimated to be around 6 billion times that of our Sun. Despite extensive research, the precise location where these jets originate in relation to the black hole remains a subject of scientific inquiry.
Understanding the Jets of M87
The jets from M87 have been a focal point for astronomers because of their extraordinary length and energy. They are not just fascinating phenomena; they provide critical insights into the mechanics of black holes and their influence on surrounding matter. Observations have shown that the jets are capable of transporting matter and energy across vast distances, impacting the intergalactic environment.
Ongoing studies aim to identify the mechanisms behind the jet formation. Researchers utilize various observational techniques, including radio and optical imaging, to analyze the jets’ properties and behavior. Notably, the Event Horizon Telescope collaboration has provided unprecedented views of M87’s black hole, allowing scientists to investigate its surroundings in detail.
The Importance of Continued Research
Understanding the jets from M87 is not merely an academic pursuit; it has implications for broader astrophysical theories and models. The dynamics of such jets may help explain similar phenomena observed in other galaxies, thereby enhancing our comprehension of the universe’s evolution.
As researchers continue their investigations, they hope to uncover the mysteries of jet formation and refine their understanding of black hole physics. The findings could lead to significant advancements in the field of astrophysics, revealing more about the complex interplay between black holes and their host galaxies.
In conclusion, the ongoing exploration of the jets from M87’s supermassive black hole underscores the importance of scientific inquiry in unraveling the complexities of our universe. Further studies promise to enhance our knowledge and may pave the way for new discoveries in the realm of astrophysics.