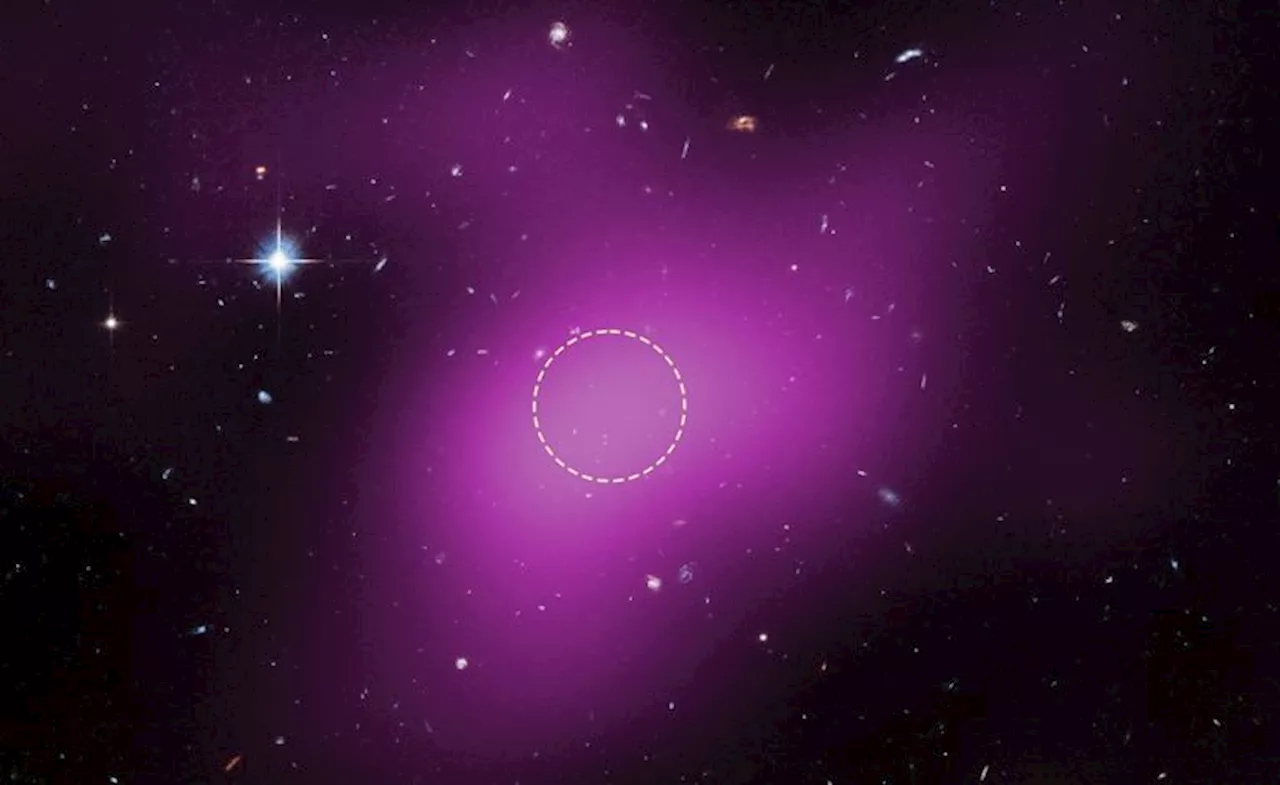
NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope has made a groundbreaking discovery, unveiling a newly identified cosmic object known as Cloud-9. This unique formation, located approximately 14 million light-years from Earth, is a cloud of gas and dark matter that challenges established theories on galaxy formation. Unlike typical galaxies, Cloud-9 contains no stars, rendering it nearly invisible in optical light.
Astronomers describe Cloud-9 as a “failed galaxy,” a term used to indicate that certain conditions in the early universe allowed dark matter halos to accumulate gas without triggering the formation of stars. This finding aligns with predictions made by scientific models, and is significant for understanding the evolution of galaxies over cosmic time.
Understanding Cloud-9 and Its Implications
Principal investigator Alejandro Benitez-Llambay from the University of Milano-Bicocca expressed the importance of this discovery, stating, “This is a tale of a failed galaxy. The absence of stars is exactly what proves the theory right. It tells us that we have found a primordial object that hasn’t yet — or may never — lit up the cosmos with starlight.” This assertion highlights the uniqueness of Cloud-9 as an object that has remained largely undetected until now.
The discovery was made possible through a collaboration between Hubble’s Advanced Camera for Surveys and ground-based observations from the Very Large Array, which indicated the presence of the cloud through diffuse radio emissions. The data revealed a faint concentration of gas, dominated by dark matter, confirming the existence of a category of astronomical objects theorized by scientists known as Reionization-Limited H I Clouds (RELHICs).
According to NASA, the conditions that led to the formation of Cloud-9 reflect a critical phase in the early universe. Some dark matter halos were able to gather gas but failed to ignite star formation, resulting in these rare, starless relics. Cloud-9 serves as a vital piece of evidence for cosmological models, providing insights into how galaxies can begin their existence—or, in this case, how they can fail to do so.
The implications of this discovery extend beyond just the identification of a new cosmic entity. It offers a rare glimpse into the processes that shaped the universe in its infancy, revealing the complexities of galaxy formation and the role of dark matter. As scientists continue to explore the mysteries of the cosmos, findings like Cloud-9 will undoubtedly contribute to a deeper understanding of our universe’s history.
This significant discovery was highlighted in various astronomy reports, underscoring the excitement within the scientific community. As researchers delve deeper into the characteristics of Cloud-9, it may pave the way for further revelations about the nature of galaxies and the fundamental forces at play in the universe.