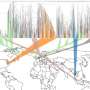
The development of innovative machine-learning models is offering new insights into the evolving landscape of antimicrobial resistance (AMR). These advanced models aim to better understand and predict patterns of resistance, a critical challenge that poses significant risks to global health. In 2019, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) was responsible for over 100,000 deaths worldwide linked to AMR, highlighting the urgent need for effective strategies to combat this crisis.
Understanding Antimicrobial Resistance
Antimicrobial resistance occurs when bacteria, viruses, fungi, or parasites evolve and become resistant to medications that once effectively treated them. The World Health Organization (WHO) identifies AMR as one of the top ten global public health threats, emphasizing its impact on healthcare systems and antibiotic treatments. As resistance increases, common infections become harder to treat, leading to longer hospital stays, higher medical costs, and increased mortality.
The rise of AMR has been exacerbated by various factors, including the overuse of antibiotics in both humans and livestock, insufficient infection prevention measures, and lack of new antibiotic development. The healthcare community is increasingly recognizing the need to address these issues through innovative research and technology.
Machine-Learning as a Game Changer
Recent research from institutions specializing in health and technology has led to the creation of machine-learning models that analyze vast datasets to track the emergence and spread of resistant strains. These models utilize data from various sources, including patient records, antibiotic usage statistics, and genomic sequencing, to provide a comprehensive overview of AMR trends.
By identifying patterns and predicting future outbreaks, these machine-learning tools can support public health initiatives and inform treatment guidelines. For instance, the models can assist healthcare providers in making informed decisions about antibiotic prescriptions, thereby preserving the effectiveness of existing treatments.
The implications of these technological advancements are profound. They not only enhance understanding of AMR dynamics but also empower healthcare systems to respond more effectively to outbreaks. As resistance patterns evolve, timely access to accurate data is crucial for managing public health threats.
In addition to improving clinical outcomes, the integration of machine-learning models into AMR research may stimulate investment in new antibiotic development. Pharmaceutical companies can leverage these insights to identify promising compounds and prioritize research efforts, potentially leading to the discovery of new treatments.
As the global health community grapples with the challenges posed by AMR, the role of technology will only continue to grow. The successful application of machine-learning models provides a hopeful outlook on managing and mitigating the impact of antimicrobial resistance. In an era where effective treatments are dwindling, these innovations offer a critical pathway toward safeguarding public health.
In summary, the emergence of machine-learning models represents a significant advancement in the fight against antimicrobial resistance. By harnessing the power of data and technology, researchers and healthcare professionals can work collaboratively to address one of the most pressing health crises of our time.