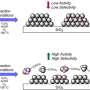
A research team from Rice University has made significant strides in understanding the behavior of molecular structures on industrial catalysts. Their findings could lead to reduced emissions and a more stable supply of essential materials used in everyday products. This research focuses on the production of vinyl acetate monomer (VAM), a vital component in adhesives, paints, coatings, and textiles.
The study highlights how these tiny molecular structures function during the manufacturing process of VAM. Understanding their behavior can pave the way for more efficient catalytic processes, ultimately leading to decreased environmental impact. The implications of this research extend across various industries, which rely heavily on VAM for the production of a wide range of goods.
Significance of the Findings
The implications of this research are manifold. Industrial catalysts play a crucial role in the production of chemicals and materials. By improving their efficiency, manufacturers can not only cut emissions but also stabilize supplies of critical materials. This is particularly important given the increasing demand for sustainable practices in manufacturing.
The findings are timely, as industries face mounting pressure to reduce their carbon footprints. The production of VAM is essential for many everyday products, making advancements in this area crucial for both environmental and economic reasons. The ability to optimize catalytic processes could lead to substantial reductions in greenhouse gas emissions, benefiting global climate efforts.
Future Applications and Research Directions
The research opens doors to further exploration in the field of catalysis. Future studies may focus on refining these molecular structures to enhance their performance, potentially leading to even greater efficiencies in VAM production. This could also stimulate innovation in developing new catalysts that are not only more effective but also environmentally friendly.
As industries continue to seek ways to balance production needs with sustainability goals, the work conducted by the Rice University team will be pivotal. Their research not only contributes to scientific understanding but also aligns with global efforts to promote greener industrial practices.
In conclusion, the insights gained from this study at Rice University may significantly influence the future of production processes across various sectors. By enhancing the efficiency of catalysts, the team is helping to pave the way toward a more sustainable and environmentally responsible industrial landscape.