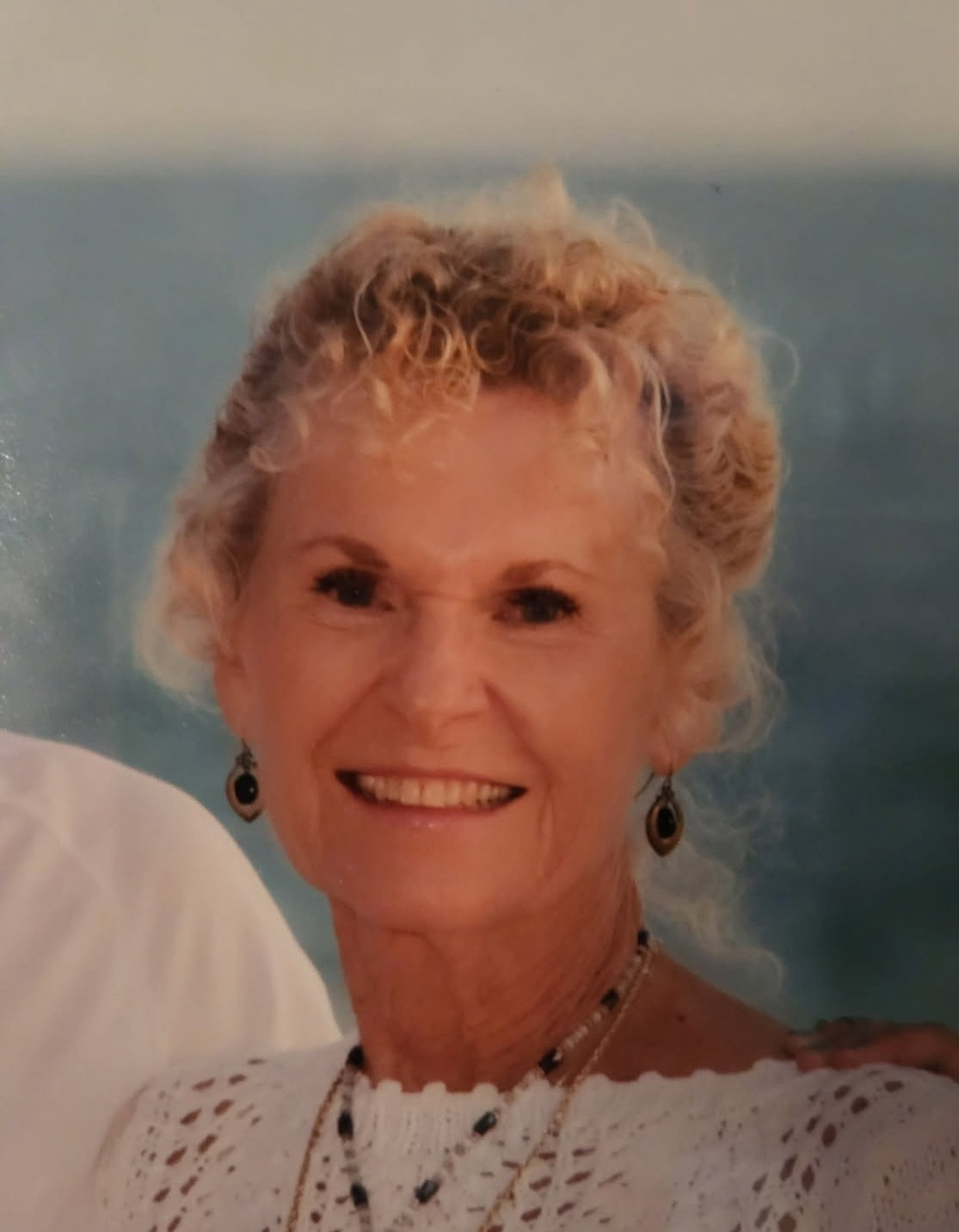
The introduction of humanoid robots in educational settings is reshaping the dynamics of interaction between students and technology. A recent study conducted by researchers at SWPS University has found that elementary school children generally respond to these robots with courtesy and empathy. Notably, the research indicates that younger children and girls are particularly inclined to attribute human-like qualities to these robotic figures.
The study involved observing children’s interactions with humanoid robots across various elementary schools. Researchers aimed to assess whether the presence of robots influences children’s behavior, particularly in terms of politeness and emotional responses. The findings reveal a significant trend: most children treat robots with respect and kindness, often engaging in polite conversation and displaying empathy towards them.
Children’s willingness to interact positively with robots may stem from their developmental stage. The research highlights that younger children, aged between five and eight, are more likely to see robots as social beings. This tendency is particularly pronounced among girls, who often exhibit greater emotional engagement during these interactions. The study suggests that this could be due to socialization patterns, where girls are generally encouraged to express empathy and kindness more than boys.
The implications of these findings are profound. As educational institutions increasingly integrate technology into the classroom, understanding how children relate to robots can inform teaching strategies. The positive interactions could foster an environment that promotes not only technological literacy but also social skills, such as empathy and cooperation.
Moreover, researchers suggest that these findings could pave the way for the development of more sophisticated educational robots that can further enhance learning experiences. By programming robots to respond to children’s emotional cues, educators could create an interactive learning environment that adapts to students’ needs and enhances their educational journey.
This research aligns with broader trends in educational technology, where the focus is shifting toward creating more engaging and supportive learning environments. As robots become more commonplace in classrooms, understanding their impact on young minds will be crucial for educators and developers alike.
In summary, the study from SWPS University underscores a significant observation: children not only interact with humanoid robots but do so with a sense of politeness and empathy. These interactions provide valuable insights into the potential of robots as educational tools, capable of nurturing social and emotional skills alongside traditional learning.